What Are Insulin Pumps?
Insulin pumps are devices used to treat certain cases of diabetes mellitus. Insulin is the molecule that allows glucose to enter the body’s cells. Glucose, in turn, is the basic nutrient that cells need for energy.
What happens with diabetes is that the body cannot make or use insulin. As a result, blood sugar levels rise above the right concentration. This is what causes all the symptoms and complications of the disease.
An insulin pump is very useful for people who have poor glucose control or for those who need more flexibility in everyday life, such as athletes. In this article, we explain how they work and their pros and cons.
How does an insulin pump work?
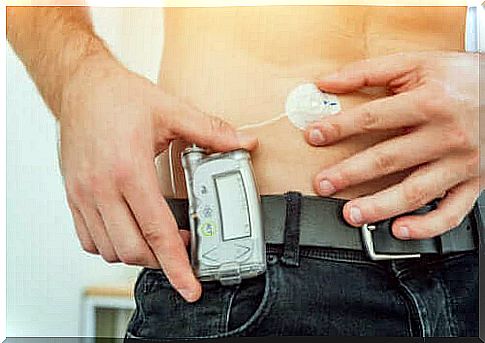
An insulin pump is a small device that is programmed to deliver insulin to the adipose tissue under the skin. It is also called a device for continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion.
For many diabetics, especially type 1 diabetics, treatment is based on the administration of insulin by subcutaneous injections. The problem is that patients must follow strict monitoring routines to avoid uncontrolled glucose levels.
The insulin pump, as explained in an article from the Clínica Universidad de Navarra, automatically administers insulin basally and before meals. This avoids the need for the patient to perform the injections.
This device is programmed according to the patient’s specific needs. In other words, the doses and the frequency of administration are programmed according to a prior examination of each case of diabetes.
The parts for insulin pumps
Insulin pumps, as mentioned above, are small units. It is important to emphasize that they are not smart devices; they must be pre-programmed to perform their function.
The pump works with a small electric motor. This motor, through a kind of piston, pushes the fabric cartridges into the tissue. According to an article in Diabetes Education Online, most pumps contain a reservoir of insulin, a battery, a monitor and the pump mechanism.
Insulin pump users can place the device outside the body and connect it to the subcutaneous tissue using a catheter with a Teflon cannula. They can carry the insulin pump themselves on a belt designed for this purpose or even carry it in a pocket.
When are insulin pumps needed?
An insulin pump may be needed to improve control of certain cases of type 1 diabetes. As an article in Medtronic explains, they are often useful when a patient is unable to achieve good glucose control despite already being in intensive care.
Many patients who receive regular insulin treatment experience frequent episodes of hypoglycaemia. This is also an indicator of poor control, so the pump can be useful.
Diabetics who need low doses can use insulin pumps. In the same way , there is optional treatment for those who require flexibility in their routine.
For example, people who can not give the attention needed to inject this molecule in a conventional way. This is the case with many athletes and women.
Women planning to become pregnant, as well as patients with diabetic neuropathy, are also candidates for this treatment. However, insulin pumps require the patient to meet certain requirements.
It is important that they are involved in disease management and are interested in good glycemic control. In addition, the patient must learn to use the pump and perform enough daily blood glucose monitoring.
Benefits of insulin pumps
Insulin pumps, as one article mentions, have many benefits. They allow very effective control of the insulin dose.
Thanks to them, very small steps can be done, which is very useful for children.
In addition, diabetics can program the basal insulin rate at different rates, depending on the time of day. For example, it can be set higher earlier in the day and lower throughout the night. This reduces the risk of hypoglycaemia.
In addition, insulin pumps make it possible to make temporary changes to the basal insulin. This is very useful for variations in the routine. For example, when you go on a trip, as this can force changes in your diet.
Disadvantages
While it may seem that insulin pumps have only advantages, the truth is that they are not without their disadvantages. First, they are external devices, which must remain permanently connected to the body through the catheter.
They can never be removed, not even to sleep. This is why many people feel uncomfortable connecting to the device. In addition, some also believe that it has an aesthetic impact, as it can be felt through clothing.
The catheter may become clogged or the pump itself may fail. This means that the patient loses glycemic control at that moment. As such, it is also important for people who use the pump to perform frequent daily tests.
Care and recommendations
Insulin pumps require the patient to be aware of their disease and to be responsible for treatment. This is because a number of measures are needed to take care of the device.
As explained by the Diabetes Foundation, the subcutaneous catheter must be replaced every 2 to 3 days. Since it is a foreign body that is connected to the subcutaneous tissue, there is a risk of infection. Therefore, to replace the catheter, it is necessary to follow some specific steps.
The first thing the user must do is wash their hands thoroughly to be as aseptic as possible. They need to change the area where they insert the catheter from time to time, otherwise the insulin may not be absorbed properly.
It is usually located at different points in the abdomen. It is necessary to check that the catheter is in good condition and to fill the pump syringe without leaving air bubbles inside.
They must also disinfect the skin on the stomach. After inserting the catheter, they tape it down to ensure that it does not move from that area. They must remove the insulin from the refrigerator approximately 24 hours before refilling.
Insulin pumps require responsibility
Although it may seem that this device is the solution for treating diabetes, this is not always the case. It is a very useful form of treatment, but it requires that the patient is aware of the treatment and knows how to handle it.
For this reason, the patient and a physician must make the decision to fit an insulin pump together. It is important that a number of requirements are met for it to be useful.