Ankylosing Spondylitis: Diagnosis And Treatment
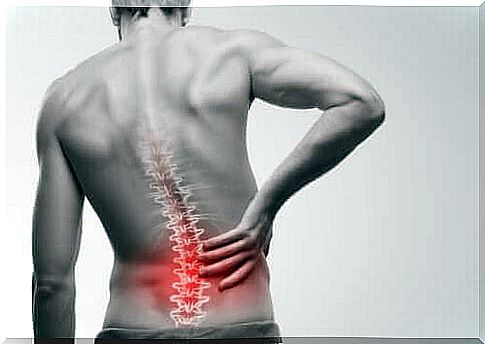
Ankylosing spondylitis, or ankylosing spondylitis, is a chronic inflammatory disease that primarily affects the facet joints. These joints tend to fuse, leading to a decrease in mobility. As a result, the back becomes less flexible. It is for this reason that people with this condition end up with a poorer posture.
No one knows exactly what causes this disease, but DNA plays an important role. Most people with Ankylosing Spondylitis have the HLA-B27 gene. However, only a few with this gene develop the disease.
The symptoms of Ankylosing Spondylitis

This rheumatic disease causes outbreaks of inflammation in the facet joints. However , there may be inflammation in other joints such as those found in the shoulders, hips, knees or ankles.
The first symptoms of Ankylosing Spondylitis include pain and stiffness in the lower back. However, this occurs mainly in the morning and after periods of inactivity. Neck pain and fatigue are also common.
Some of the most affected areas are the facet joints between the spine, pelvis and hip joints. However, it can also affect the points where tendons and ligaments meet the bones, especially those in the spine.
When you have Ankylosing Spondylitis, new bones are formed as part of the body’s attempts to heal. This new bone reduces the space between the vertebrae. As a result, parts of both vertebrae fuse together.
Then these parts of the spine become stiff and inflexible. Fusion can also seize the chest and reduce the capacity and function of the lungs.
Ankylosing spondylitis: Complications
Some of the complications of Ankylosing Spondylitis are:
- Ocular Inflammation (Uveitis): This is one of the most common complications of Ankylosing Spondylitis. It quickly causes pain in the eye, sensitivity to light, and blurred vision.
- Damage to the heart valves: This disease can cause problems in the main artery. The inflamed main artery can affect the shape of the aortic valve in the heart, which will change the function of the valve.
Diagnosis
There are several identifiable symptoms of Ankylosing Spondylitis. These include:
- Clinical symptoms such as low back pain lasting over three months. It can improve with exercise, but does not disappear with rest. You must also take into account the limitation of thoracic dilation, as well as the mobility of the spine.
- Radiological evidence of inflammation of the iliosacral joints.
Depending on the criteria found in the patient, a diagnosis of ankylosing spondylitis will either be defined through a clinical criterion and a radiologist, or made probable in case a person presents three clinical or one radiological criteria.
Blood and urine tests may help support the diagnosis of the presence of the HLA-B27 antigen in the blood. They can also determine the intensity of the inflammatory process that can plague a person.
Treatment of Ankylosing Spondylitis
The treatment of Ankylosing Spondylitis combines various pharmacological alternatives and rehabilitation.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and painkillers. These are pharmacological treatments, aimed at controlling pain and reducing or suppressing arthritis. As a result, the patient’s quality of life improves. By relieving discomfort, they improve the rest of the night.
- Disease-modifying medications. These act on the immune system itself.
- Biological medicines. Although these medications do not cure the conditions, they do control the symptoms of this disease in many people.
- Rehabilitation. You need to do rehabilitation exercises continuously, along with pharmacological treatments. Physical and breathing exercises improve mobility in the spine and muscle strength.
- You should also do gentle exercises that strengthen your back, such as swimming.
- Surgery. Surgery is rarely used, and usually only when the joints are severely damaged and mobility is almost lost.
When mixing and matching possible treatments, you can avoid stiffness. They can also help you prevent other muscle and locomotor dysfunctions.
We hope you enjoyed this article. You can also enjoy reading about fibromyalgia and how to treat it: