What Are The Uses Of An Antibiogram?
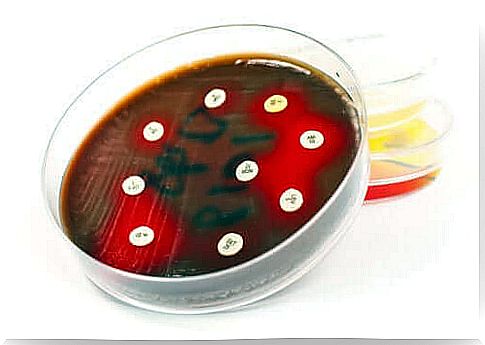
An antibiogram provides information to a doctor so that they know exactly which drug to prescribe. This is because the different types of bacteria do not react equally to the same antibiotics. In the same way, medicines are different and only attack a certain type of infectious agent.
OK, but why is it that not all microorganisms fall for the same antibiotic? This is a common question, and the answer lies in the concept of evolution. This is because microorganisms evolved to have mechanisms to avoid substances that prevent them from surviving.
We need to know these resistances in advance in order to apply appropriate treatment to the infected person. For this purpose, the antibiogram reveals the sensitivity of a given bacterium to certain antibiotics.
Resistance to antibiotics
Bacteria become resistant over time, based on their need to survive. Drug resistance, which we can observe in antibiograms, has two categories:
- Congenital mechanisms that a bacterial family has naturally entered into the genetic code (they already had it before the use of antibiotics)
- Acquired mechanisms by which certain bacteria created methods to resist or combat antibiotics (they went from being sensitive to these substances to being resistant)
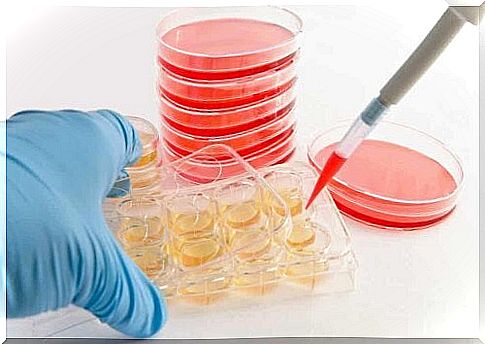
An example of acquired resistance
An example of acquired resistance is what happened after the discovery of penicillin by Alexander Fleming. Penicillin was the most important antibiotic in the 1940s, but a bacterium called Staphylococcus aureus soon developed resistance.
Penicillin is an antibiotic that binds to an enzyme generated by the bacterial wall. In other words , this substance inhibits the synthesis of the bacterial wall, leaving the microorganism unprotected and leading to its death. However , Staphylococcus aureus produced enzymes called penicillinases to break down the penicillin molecule.
Dangers of antibiotic resistance
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) wrote a report from 2019 on the threat of antibiotic resistance in the United States, and shows that the number of resistances is still high. There are currently 2.8 million antibiotic-resistant infections.
Looking at all these data, the threat from antibiotic resistance is worrying and frightening. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), the use and misuse of antimicrobials has increased the number and types of resistant microorganisms in recent years.
What is an antibiogram?
This is a test that helps us determine the most appropriate antibiotic preparation to specifically counteract the infectious bacteria. A doctor pulls a sample from the area of infection to isolate the causative microorganism when a person has an infection.
The microorganism then grows in a controlled medium, a culture, to determine what type of bacteria it is and what family it belongs to. Once this step is done, laboratory technicians grow it in another medium with antibiotic-releasing tablets.
The bacteria grow in this new culture, but those who are sensitive to antibiotics leave a halo around the tablet. This halo indicates that the bacteria were not able to reproduce because antibiotics prevented it.

Treatment according to an antibiogram
A very serious infection does not allow you to wait for the results of an antibiogram. Based on the patient’s characteristics, focus on infection, and whether the infection was applied outside or inside the hospital, the patient is treated with broad-spectrum antibiotics.
These broad-spectrum drugs cannot be deliberately used on anyone who has an infection. This is because their use involves the risk of resistance. Of course, there is no problem if they become resistant, as we would not be able to use the same antibiotic in severe infections.
On the other hand, targeted treatment is that which is tailored to the bacteria in question. It is determined by the antibiogram, which indicates which antibiotic to use.
Avoid bacterial resistance
Prevention of bacterial resistance is necessary and essential for humanity. Furthermore, therapy will be ineffective and the consequences serious if microorganisms become too resistant.
Advice number one is to take the correct dose of prescribed antibiotics according to the doctor’s instructions. You can not stop taking the medicine even if you feel better, nor can you change the dose according to your personal taste.
Using an antibiogram will be the norm if you encounter a resistant bacterium, despite any precautions you can take. It is a powerful biochemical tool for treating serious infectious cases.